Ligation-mediated PCR protocols have various makes use of together with the identification of integration websites of insertional mutagens, integrating vectors and naturally occurring cellular genetic parts.
For approaches that make use of NGS sequencing, the relative abundance of integrations inside a posh combination is usually decided by using learn counts or distinctive fragment lengths from a ligation of sheared DNA; nevertheless, these estimates could also be skewed by PCR amplification biases and saturation of sequencing protection.
Right here we describe a modification of our earlier splinkerette primarily based ligation-mediated PCR utilizing a novel Illumina-compatible adapter design that stops amplification of non-target DNA and incorporates distinctive molecular identifiers. This design reduces the variety of PCR cycles required and improves relative quantitation of integration abundance for saturating sequencing protection.
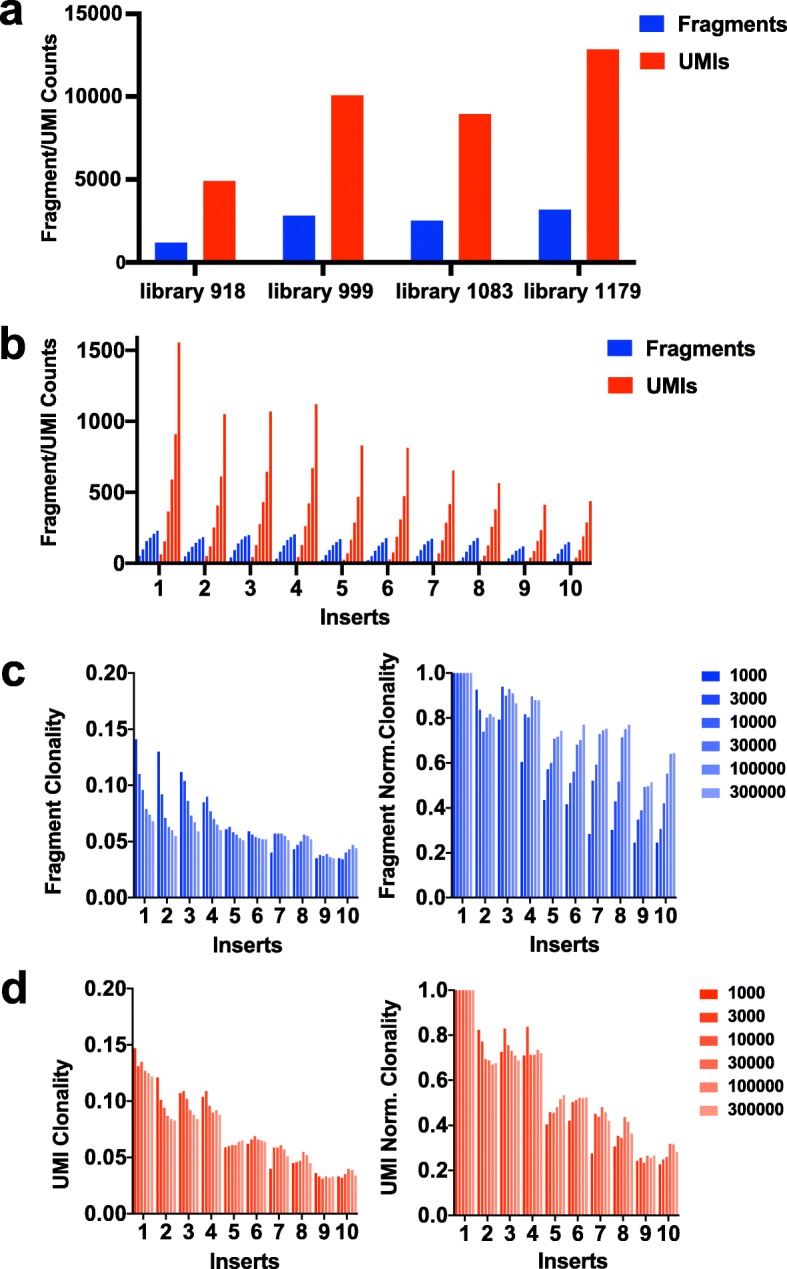
By inverting the forked adapter strands from a normal orientation, the integration-genome junction might be sequenced with out affecting the sequence variety required for cluster era on the move cell. Replicate libraries of murine leukemia virus-infected spleen samples yielded extremely reproducible quantitation of clonal integrations in addition to a deep protection of subclonal integrations.
A dilution collection of DNAs bearing integrations of MuLV or piggyBac transposon exhibits linearity of the quantitation over a spread of concentrations.
Merging ligation and library era steps can cut back whole PCR amplification cycles with out sacrificing protection or constancy. The protocol is powerful sufficient to be used in a 96 properly format utilizing an automatic liquid handler and we embrace packages to be used of a Beckman Biomek liquid dealing with workstation.
We additionally embrace an informatics pipeline that maps reads, builds integration contigs and quantitates integration abundance utilizing each fragment lengths and distinctive molecular identifiers. Strategies for optimizing the protocol to different goal DNA sequences are included.
The reproducible distinction of clonal and subclonal integration websites from one another permits for evaluation of populations of cells present process choice, resembling these present in insertional mutagenesis screens.
LUMI-PCR: an Illumina platform ligation-mediated PCR protocol for integration site cloning, provides molecular quantitation of integration sites.
Marine bacterial communities within the higher gulf of Thailand assessed by Illumina next-generation sequencing platform.
The whole bacterial group performs an vital function in aquatic ecosystems. On this research, bacterial communities and variety alongside the shores of the Higher Gulf of Thailand have been first characterised. The affiliation between bacterial communities and kinds of land use was additionally evaluated.
The bacterial communities and variety of seawater within the Higher Gulf of Thailand, with regard to kinds of land use, have been first revealed through the use of Illumina next-generation sequencing. A complete of 4953 OTUs have been noticed from all samples through which 554 OTUs have been widespread.
The bacterial communities in sampling websites have been considerably completely different from one another. The run-off water from three kinds of land use considerably affected the group richness and variety of marine micro organism. Aquaculture websites contained the very best ranges of group richness and variety, adopted by mangrove forests and vacationer websites.
Seawater physicochemical parameters together with salinity, turbidity, TSS, whole N, and BOD5, have been considerably completely different when grouped by land use. The bacterial communities have been primarily decided by salinity, whole N, and whole P. The species richness estimators and OTUs have been positively correlated with turbidity. The highest ten most plentiful phyla and genera in addition to the distribution of bacterial courses have been characterised.
The Proteobacteria constituted the most important proportions in all sampling websites, ranging between 67.31 and 78.80%. The numbers of the Marinobacterium, Neptuniibacter, Synechococcus, Candidatus Thiobios, hgcI clade (Actinobacteria), and Candidatus Pelagibacter have been considerably completely different when grouped by land use.Kind of land use considerably affected bacterial communities and variety alongside the Higher Gulf of Thailand. Turbidity was essentially the most influential parameter affecting the variation in bacterial group composition. Salinity, whole N, and P have been those of the vital elements that formed the bacterial communities.
As well as, the variations of bacterial communities from site-to-site have been better than within-site. The Proteobacteria, Bacteroidetes, Actinobacteria, Cyanobacteria, Verrucomicrobia, Euryarchaeota, Planctomycetes, Firmicutes, Deep Sea DHVEG-6, and Marinimicrobia have been essentially the most and customary phyla distributed throughout the Higher Gulf of Thailand.