Abstract
Cardiovascular Recombinant human erythropoietin (rHuEPO) treatment has solved the problem of anaemia in dialysis patients. However, its application to predialysis patients has raised some doubts about its effects on the progression of kidney disease and on the regulation of blood pressure (BP) and hemodynamics. We have prospectively studied for at least 6 months a group of 11 pre-dialysis patients treated with rHuEPO (initial dose, 1000 U subcutaneously three times a week). Clinical evaluation and biochemical and haematological measurements were performed once every 2 weeks.
Twenty-four-hour ambulatory BP monitoring, echocardiography, and determination of neurohumoral mediators of hemodynamics were performed once every 3 months. An adequate hematological response was found (hemoglobin, 11.7 +/- 0.4 g/dL v 9 +/- 0.3 g/dL) without changes in the progression of kidney disease. A decrease in cardiac output and an increase in total peripheral resistance were observed as anaemia improved. There was a trend toward decreased left ventricular (LV) thickness and a significant decrease in LV mass index (from 178.2 +/- 20.6 g/m2 to 147.3 +/- 20.6 g/m2). /m2).
Blood pressure control did not improve; In addition, in some patients, an increase in systolic values was detected by ambulatory BP. Casual BP was apparently stable. Sequential determinations of neurohumoral mediators of hemodynamic substances (endothelin, renin, norepinephrine, epinephrine, dopamine) failed to explain these results. Ambulatory BP reveals worse control in some previously hypertensive patients and confirms the usefulness of this technique in the assessment of patients receiving erythropoietin treatment.
The trend toward regression of LV hypertrophy without better BP control confirms the role of anaemia among the multiple factors leading to LV hypertrophy in ESRD and opens therapeutic possibilities. Better BP control can potentially offset the beneficial effects that correcting anaemia would have on the cardiovascular system.
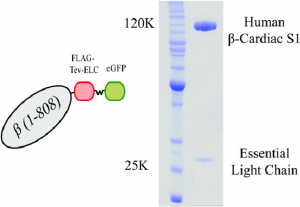
Purity: Greater than 90% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
Target Names: VEGFC
Uniprot No.: P49767
Research Area: Cancer
Alternative Names
Flt 4L; Flt4 ligand; FLT4 ligand DHM; Flt4-L; Flt4L; Vascular endothelial growth factor C; Vascular endothelial growth factor-related protein; Vascular endothelial growth factor-related protein; VEGF C; VEGF-C; Vegfc; VEGFC_HUMAN; PVR
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: E.coli
Expression Region: 112-227aa
Mol. Weight: 40.1kDa
Protein Length: Full Length of Mature Protein
Tag Info: N-terminal GST-tagged
Form: Liquid or Lyophilized powder
Note:
We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirements for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand.
Buffer
If the delivery form is liquid, the default storage buffer is Tris/PBS-based buffer, 5%-50% glycerol.
Note: If you have any special requirements for the glycerol content, please remark when you place the order. If the delivery form is a lyophilized powder, the buffer before lyophilization is Tris/PBS-based buffer, 6% Trehalose, pH 8.0.
Reconstitution
We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL. We recommend adding 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20°C/-80°C. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as a reference.